Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Fatty Liver?
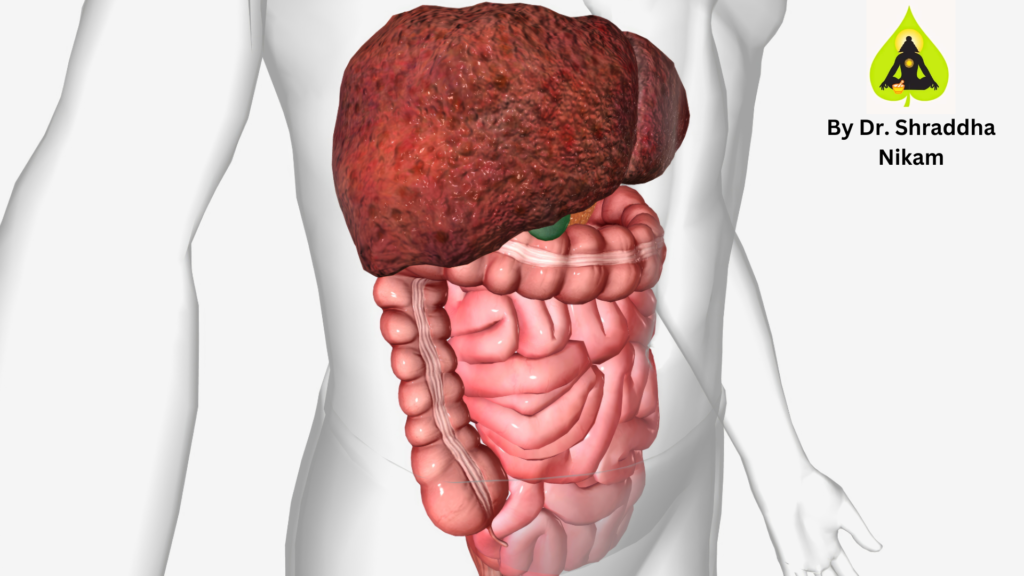
Hepatic steatosis is an alternative term for fatty liver. Fat buildup in the liver cells is a defining feature of this illness. Ayurvedic Fatty Liver Treatment uses internal medication, Panchakarma therapies, and a healthy diet to support liver function.
A common liver condition known as “fatty liver” can have several origins, such as non-alcoholic reasons (also known as “non-alcoholic fatty liver disease,” or NAFLD) or excessive alcohol use (also known as “alcoholic fatty liver disease”).
The most prevalent kind of fatty liver, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is characterized by fat accumulation in the liver cells even in the absence of heavy alcohol use. Obesity, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and other disorders linked to unhealthy lifestyle choices are frequently linked to it.
Fat buildup in the liver can lead to inflammation and damage to liver cells, which can result in liver dysfunction and could worsen existing disorders like cirrhosis, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and liver fibrosis.
Ayurvedic view about fatty liver:
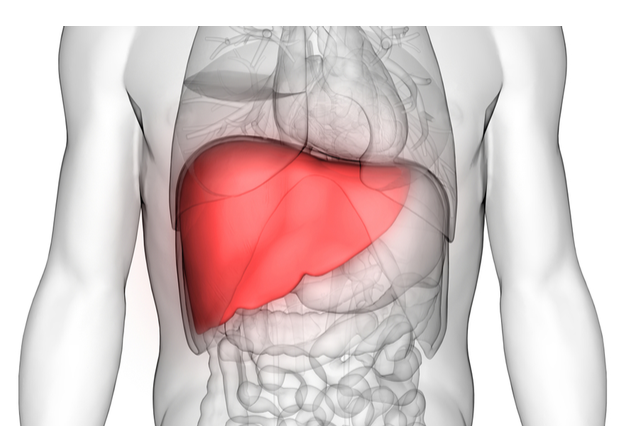
According to Ayurveda, fatty liver is a condition caused by an imbalance between the doshas of Pitta and Kapha. Ayurvedic teachings state that the build-up of toxins (Ama) in the body is a result of poor digestion, a sedentary lifestyle, and an unhealthy diet. Fatty liver can develop as a result of these toxins and worsened Pitta and Kapha doshas. The main goals of Ayurvedic treatment for fatty liver are liver detoxification, better digestion, and Pitta and Kapha dosha balance and pacification
Causes of fatty liver:
Prior to beginning an ayurvedic treatment for fatty liver, one must be aware of the causes of the condition.
The following is a list of some typical causes of fatty liver:
- Poor diet: Eating a diet high in processed foods, refined carbs, trans-fats, and added sugars can cause the development of a fatty liver. These poor eating decisions may cause the liver to get fatter.
- Metabolic syndrome and obesity: Obesity and excess weight are significantly linked to fatty liver. Being overweight raises the chance of developing fatty liver, particularly in the abdominal region. Fatty liver is also more common in those with metabolic syndrome, a condition that combines high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, and insulin resistance.
- Alcohol Consumption: One of the main causes of fatty liver is excessive alcohol consumption. Alcohol’s harmful effects on liver cells cause fat to build up and inflammation, which results in alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes: Fatty liver can develop as a result of insulin resistance, a disease in which the body’s cells become less receptive to insulin. People with type 2 diabetes or other metabolic illnesses frequently experience it.
- Medications: A number of pharmaceuticals, including antiretroviral drugs used in HIV treatment, tamoxifen, corticosteroids, and methotrexate, can cause fatty liver.
- Quick Weight Loss: Crash dieting or rapid weight loss might cause the liver to become overly fat. This condition is referred to as starvation-induced fatty liver or acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP) in pregnant women.
- Genetics: A genetic propensity to develop fatty liver may exist in some individuals. The way the body breaks down fats can be impacted by specific genetic abnormalities, which can also lead to the buildup of fat in the liver.
- Other Medical Conditions: In addition to hepatitis C, Wilson’s disease, a hereditary ailment affecting copper metabolism, and some inherited metabolic diseases can also result in fatty liver.
- It’s crucial to remember that the most prevalent kind of fatty liver, known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is frequently linked to metabolic syndrome, obesity, and insulin resistance. But people without these risk factors or who are not obese can also develop fatty liver.
Symptoms of fatty liver:
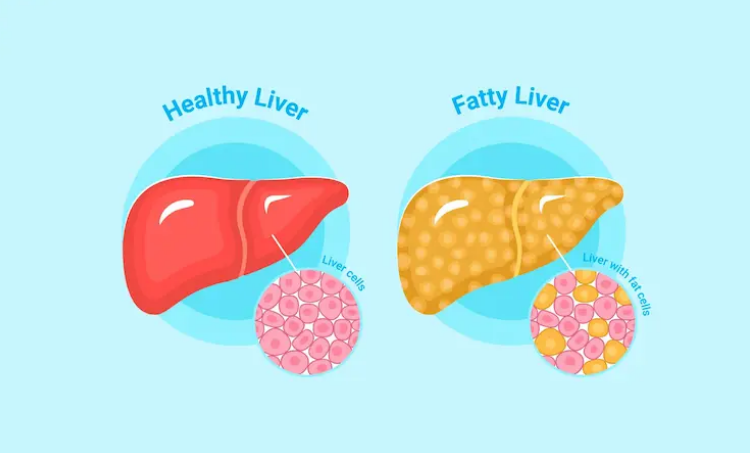
Fatty liver frequently doesn’t exhibit any symptoms when it first starts. However, people may have a variety of symptoms as the illness worsens or if complications develop. The following are a few typical signs of fatty liver:
- Fatigue: Common signs of fatty liver include chronic fatigue and a generalized sense of exhaustion. Impaired liver function can impact energy metabolism and cause weariness to rise.
- Pain or Discomfort in the Upper Right Abdominal Area: A few people with fatty livers may have pain or discomfort in this area. Liver enlargement or inflammation may be the cause of this.
- Loss of Appetite or Weight Loss: Fatty liver can occasionally cause inadvertent loss of appetite or weight. Changes in metabolism or inflammation of the liver could be the cause of this.
- Weakness:General weakness or a feeling of weakness in the body may be experienced by individuals with fatty liver. This can be attributed to the liver’s compromised ability to store and release energy.
- Jaundice: Rarely, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a disorder involving inflammation and damage to the liver, can develop from fatty liver. At more advanced stages of liver disease, jaundice—a yellowing of the skin and eyes—may develop.
- Ascites: A buildup of fluid in the abdominal cavity is referred to as ascites. It frequently comes with discomfort and swelling in the abdomen and may be a consequence of severe fatty liver disease.
- Enlarged Liver: The upper right side of the abdomen may feel heavy or full in certain situations due to an enlarged liver.
Ayurvedic medicine for fatty liver:
Several herbal remedies and formulations have long been utilized in Ayurved to promote liver health and treat fatty liver.
The following are a few popular Ayurvedic treatments for fatty liver:
- Aarogyavardhini Vati: This traditional Ayurvedic remedy promotes healthy digestion and liver function. It has a blend of herbs, minerals, and metals, such as Guggulu, Amla (Indian Gooseberry), Shilajit, and Haritaki (Terminalia Chebula). It is said to support the liver’s improvement and detoxification.
- Triphala: Amalaki (Emblica officinalis), Bibhitaki (Terminalia bellirica), and Haritaki (Terminalia chebula) are the three fruits that make up Triphala. In Ayurveda, it is frequently used to treat a range of illnesses, including liver problems. Triphala is thought to promote digestion and liver function in addition to having detoxifying qualities.
- Kutki, also known as Picrorhiza Kurroo, is a bitter herb that is used in Ayurveda to treat and promote liver function. It has a reputation for having hepatoprotective qualities and may aid in liver detoxification, liver function improvement, and liver inflammation reduction. After meals, take one to three grams of kakuti powder twice a day with water.
- Bhumi Amla (Phyllanthus niruri): Also referred to as the stonebreaker plant, Bhumi Amla is a popular herb in Ayurveda used to support liver function. It is thought to possess antioxidant, antiviral, and hepatoprotective qualities. Bhumi Amla may aid in liver cleansing, liver cell protection, and liver inflammation reduction. Once day, consume 10 to 20 cc of Bhumi-Amla juice.
- Punarnavadi Kashayam: An Ayurvedic herbal concoction called Punarnavadi Kashayam is used to treat and maintain liver function in a variety of liver conditions. Herbs like Musta (Cyperus rotundus), Guduchi (Tinospora Cordifolia), and Punarnava (Boerhavia Diffusa) are included in them. It is thought to possess hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, and diuretic qualities.
Ayurvedic home remedies for fatty liver:

To maintain liver health and manage fatty liver, there are a number of Ayurvedic home remedies for fatty liver are as follows:
- Lemon Water: To start the day, squeeze half a lemon juice into a glass of warm water. Lemon water aids the detoxification process and stimulates liver function.
- Turmeric Milk: To make a warm beverage, mix half a teaspoon of powdered turmeric into a cup of heated milk. Curcumin, an ingredient in turmeric, has anti-inflammatory and liver-protective qualities.
- Aloe Vera Juice: Take 1-2 teaspoons of fresh aloe Vera juice first thing in the morning when you’re not hungry. Aloe Vera can promote liver health and has the ability to detoxify the liver.
- Ginger Tea: To make ginger tea, boil a few fresh ginger slices in water for ten to fifteen minutes. Ginger can help with liver and digestive function and contains anti-inflammatory qualities.
- Papaya: Consume ripe papaya on a daily basis to improve liver function and aid with digestion. It includes enzymes. Papaya can be had as a snack or as part of your breakfast.
- Indian Gooseberry (Amla): Regularly consume Amla juice or fresh Indian gooseberries. Antioxidants and vitamin C, which are abundant in Amla, can help shield the liver from harm.
- Triphala Powder: Known for its cleansing qualities, Triphala is a blend of three fruits: Amalaki, Bibhitaki, and Haritaki. Before going to bed, mix one teaspoon of Triphala powder with some warm water and drink it to help with digestion and liver health.
- Kokum Juice: Garcinia Indica enhances the performance of the liver.
- Radish juice: To help with fatty liver, you can include radish (Raphnas Sativus) vegetables in your diet or drink their juice. Recommended dosage for juice is 10-20ml per day.
Role of panchakarma in ayurvedic treatment for fatty liver:

Ayurvedic panchakarma is a traditional detoxification and rejuvenation treatment that helps treat fatty liver. It is an all-encompassing strategy that includes a number of therapeutic procedures to get rid of toxins, balance doshas, and improve general health.
Panchakarma aids in the Ayurvedic treatment of fatty liver in the following ways:
- Thorough Detoxification: The goal of panchakarma treatments is to rid the body—including the liver—of toxins and impurities. In Panchakarma, “Vamana” (therapeutic vomiting) or “Virechana” (therapeutic purgation) are the two main detoxifying techniques. These processes aid in clearing the liver and digestive tract of excess toxins and accumulated waste.
- Dosha Balancing: Ayurveda states that disorders, such as fatty liver, might arise due to an imbalance in the doshas (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha). The goal of panchakarma treatments is to rebalance the doshas, especially Pitta dosha, which is important for liver function. Panchakarma can aid in the management of fatty liver by balancing Pitta dosha.
- Supporting Liver Function: One of the main goals of panchakarma treatments is to support liver function. One such treatment is “Basti,” or medicated enema. When used in Basti, medicinal oils or herbal concoctions aid in liver cleansing and nourishment, boosting liver health and supporting healthy liver function.
- Boosting Metabolism and Digestion: Panchakarma treatments comprise a range of procedures like Shirodhara, which is the continual application of herbal oil to the forehead, Abhyanga, which is an oil massage, and Swedana, which is a herbal steam therapy. These therapies facilitate better digestion, increase metabolism, and improve the digestive system’s general performance, which includes the liver.
- Stress Reduction: Long-term stress exacerbates fatty liver and can lead to liver dysfunction. The goal of the Panchakarma ayurvedic treatment for fatty liver is to induce relaxation and lower stress levels using techniques like meditation, soft massages, and Shirodhara. Reducing stress can benefit the health of the liver.

Here are some other guidelines for individuals with fatty liver:
- Cut Down on Saturated and Trans Fats: Eat fewer meals that are heavy in these types of fats. These consist of fried foods, processed snacks, fatty meats, full-fat dairy items, and baked goods that are produced professionally. Cooking using cold-pressed oil (Kacchi Ghani oil) and healthier techniques like steaming or grilling are the better choices.
- Place a Focus on Plant-Based Foods: Eat more fruits, vegetables, nuts, whole grains, legumes, and legume products. These foods are high in nutrients, fiber, and antioxidants, all of which promote liver health and aid in the management of fatty liver. For a spectrum of healthful components, try to eat a variety of colored fruits and vegetables.
- Minimize Refined Carbohydrates and Added Sugars:Minimize the consumption of sugary beverages, sweets, pastries, and refined carbohydrates like white bread and white rice, maida products. These foods can contribute to weight gain and worsen fatty liver.
- Healthy Diet: Consume a diet rich in whole grains, lean meats, fresh produce, healthy fats, and balanced fruits and vegetables. Steer clear of processed foods, fried foods, sugary drinks, and too much alcohol. Berries, pears, and melons are examples of cold, non-acidic foods that you can include in your diet.
- Regular Physical Activity: Take part in regular physical activities, such as yoga, brisk walking, or other exercises. Frequent exercise promotes overall liver function and aids in keeping a healthy weight.
Conclusion:

Chronic liver disease is increasingly being caused by fatty liver, which is consistent with the rising prevalence of obesity and the metabolic syndrome. A multidisciplinary strategy with distinct risk categorization is necessary for management. It is rather encouraging that ayurvedic treatments discussed in this blog post significantly improve the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver. I wish all the patients of fatty liver speedy and reversible recovery.

Good subscribed information about fatty liver and precautions for maintain healthy liver.👌👍
I was eagerly waiting for this Post. Thank you doctor. this blog cleared all my doubt about fatty liver.